Dual sensor scanning speeds slide imaging
In pathology, accurate focusing is a critical challenge of whole-slide imaging, primarily because of inherent tissue topology variability. Traditional line scanning and tile-based scanning systems are limited in their ability to acquire a high degree of focus points while still maintaining high throughput.
To solve this problem, Independent Dual Sensor (IDS) scanning has been developed by Omnyx (Pittsburgh, PA, USA; www.omnyx.com), a joint venture of GE Healthcare and the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. IDS scanning decouples image acquisition from focusing, resulting in rapid scanning while maintaining focus within each tile of a whole-slide image, thus generating higher-quality images at a fast rate.
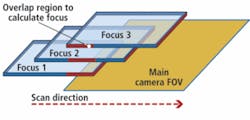
With IDS scanning, the focus sensor acquires three images in different z planes while in motion and uses the overlapping region to calculate the best focal plane. The main camera waits until the z stage moves into the correct focal plane and acquires the main image. This allows for focus calculations within each acquired image tile.