[Page 2] Life sciences imaging: Infrared cameras help analyze water absorption in crops
Editor's note: This article is continued from page one.
This camera is also used at station four, where the section of the plant above the soil is analyzed in the same manner. Captured images provide information on the water content of the stem and leaves, and by extension, on the drying process as well as the plants’ recovery following drought.
Station five
At the final station, fluorescence technology is used to highlight particular substances, such as chlorophyll, in the imaging of the plants. Plant’s pigments are stimulated using blue light with a wavelength below 500 nm, with measurement taking place above this wavelength.
Plant pots travel via conveyor belts from one station to the next, where they are imaged from different angles and from above, so that they are imaged in all dimensions.
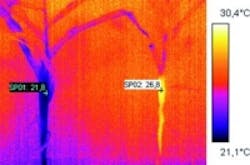
Of particular interested for bio-scientists, according to Allied Vision, is the use of infrared cameras in the SWIR (900 to 1700 nm) range. With this technology, a plant’s moisture content, or the water distribution within the plant, can be highlighted. Because water strongly absorbs infrared light in a wavelength range from 1450 to 1500 nm, it appears black and opaque in an infrared image, so that aqueous areas within a plant appear correspondingly darker. With this technology, scientists can follow water absorption from the roots into the leaves, as well as evaporation and desiccation.
Data captured in the Scanalyzer3D is analyzed and processed by LemnaTec’s software, LemnaGrid. Additionally, tools such as LemnaMiner and LemnaShare ease data export and exchange for further processing by a research team.
LemnaTec’s clients for the Scanalyzer3D include BASF, Bayer Crop Science, DuPont, and international research institutions such as ACPFG (Australia), ICAR (India), and the French national agricultural research institute, INRA.
View more information onLemnaTec.
View more information on Allied Vision cameras.
Share your vision-related news by contactingJames Carroll, Senior Web Editor, Vision Systems Design
To receive news like this in your inbox,click here.
Page 1 | Page 2
Join ourLinkedIn group | Like us on Facebook | Follow us on Twitter
About the Author

James Carroll
Former VSD Editor James Carroll joined the team 2013. Carroll covered machine vision and imaging from numerous angles, including application stories, industry news, market updates, and new products. In addition to writing and editing articles, Carroll managed the Innovators Awards program and webcasts.