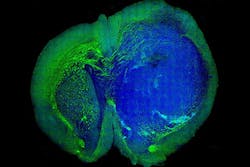
Laser imaging identifies tumors in the brain
Using a technique called stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy , a team of researchers from Harvard University and the University of Michigan were able to build images which enabled them to distinguish between microscopic areas of tumor cells and healthy tissue in the brains of mice. The technique works by shining non-invasive lasers into tissue and detecting the weak signal that emerges. By analyzing the signal’s spectrum, researchers can build images of the cellular makeup of the tissue in vivo.