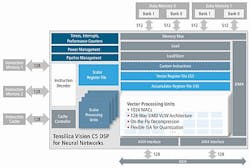
Cadence Design Systems, Inc. has announced the launch of the Cadence Tensilica Vision C5 digital signal processor (DSP), which is optimized for vision, radar and LIDAR, and fused-sensor applications with high-availability neural networkcomputational needs.
Aimed at such applications as automotive, surveillance, drone, and mobile/wearable markets, the Vision C5 DSP offers 1TMAC/sec computational capacity to run all neural network computational tasks. The DSP is architected as a dedicated neural-network-optimized DSP and accelerates all accelerates all neural network computational layers (convolution, fully connected, pooling and normalization) —not just the convolution functions—which frees up the main vision/imaging DSP to run image enhancement applications independently while the Vision C5 DSP runs inference tasks.
By eliminating extraneous data movement between the neural network DSP and the main vision/imaging DSP, said Cadence, the Vision C5 DSP provides a lower power solution than competing neural network accelerators and offers a single-processor programming model for neural networks.
"Many of our customers are in the difficult position of selecting a neural network inference platform today for a product that may not ship for a couple of years or longer," said Steve Roddy, senior group director, Tensilica marketing at Cadence. "Not only must neural network processors for always-on embedded systems consume low power and be fast on every image, but they should also be flexible and future proof. All of the current alternatives require undesirable tradeoffs, and it was clear a new solution is needed. We architected the Vision C5 DSP as a general-purpose neural network DSP that is easy to integrate and very flexible, while offering better power efficiency than CNN accelerators, GPUs and CPUs."
Jeff Bier, founder of the Embedded Vision Alliance, also commented: "The applications for deep learning in real-world devices are tremendous and diverse, and the computational requirements are challenging," he said. "Specialized programmable processors like the Vision C5 DSP enable deployment of deep learning in cost- and power-sensitive devices."
In addition to the 1TMAC/sec computational capacity, the DSP features 1024 8-bit MACs or 512 16-bit MACs; VLIW SIMD architecture with 128-way, 8-bit SIMD or 64-way, 16-bit SIMD; and is designed for multi-core designs, enabling a multi-teraMAC solution in a small footprint. Furthermore, the DSP comes with the Cadence neural network mapper toolset, which will map any neural network trained with tools such as Caffe and TensorFlow into executable and optimized code for the Vision C5 DSP.
View more information on the Vision C5 DSP.
Share your vision-related news by contacting James Carroll, Senior Web Editor, Vision Systems Design
To receive news like this in your inbox, click here.
Join our LinkedIn group | Like us on Facebook | Follow us on Twitter
Learn more: search the Vision Systems Design Buyer's Guide for companies, new products, press releases, and videos
About the Author

James Carroll
Former VSD Editor James Carroll joined the team 2013. Carroll covered machine vision and imaging from numerous angles, including application stories, industry news, market updates, and new products. In addition to writing and editing articles, Carroll managed the Innovators Awards program and webcasts.