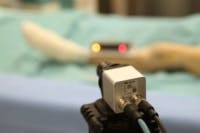
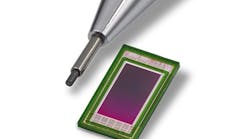
In order to develop a more accurate means for measuring patients’ legs for purposes of hip replacements, a consortium of organizations have developed a system that utilizes amachine vision camera and LED lighting.
MORE ARTICLES
Robot performs IV procedures autonomously
Digital light projector localizes treatment of skin diseases
Endoscope employs custom camera for in-vivo cancer detection
Led by the Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU, the project came to be as a result of the research team taking a look at the inaccuracies of measuring leg lengths before the an artificial hip can be surgically implanted, and the subsequent issues that can arise. For example, if a leg isn’t precisely measured and a hip is implanted, a leg can be longer or shorter than it used it be, which leads to problems with the spine, which then have to be resolved using shoe inserts.
Because of this, the Fraunhofer-led team developed a new technique that will enable orthopedic surgeons to measure their patients’ leg lengths much more precisely. In order to capture such a measurement, a patient lies down in a prone position and a physician attaches a small plastic box containing twoLED lights to the patient’s shin. The physician then lifts the patient’s leg up by the heel, and with that motion, the two lights trace an arc that is recorded by an industrial camera positioned about 1.5 meters to the side of the patient.
The camera used is aVLG-22C VisiLine GigE camera from Baumer. The VGL-22C features the 2 MPixel progressive scan CMV2000 CMOS image sensor from CMOSIS, which has a 5.5 µm pixel size and can achieve frame rates of up to 55 fps.
The principal in recording the arc that the leg traces is similar to that of a compass, according to Fraunhofer. The hip joint from which the leg "hangs," is like the point of the compass, while the LEDs act as the pencil. If the distance between the two changes (i.e. – if the leg becomes shorter or longer), that will change the arc traced by the LEDs.
Page 1 |Page 2